-blue.svg)
The bdsm package implements Bayesian model averaging (BMA) for dynamic panels with weakly exogenous regressors, following the methodology of Moral-Benito (2016). This addresses both:
The package features:
You can install the released version of bdsm from CRAN with:
install.packages("bdsm")And the development version from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("mateuszwyszynski/bdsm")Once installed, simply load the package:
library(bdsm)Your data should be in the following format:
year),country),gdp),A convenience function join_lagged_col() can help
transform a dataset that already contains both a variable and its lagged
version into the required format.
You can also use feature_standardization() to perform
mean-centering, demeaning (entity/time effects), or scaling
(standardization) as needed. For example:
library(magrittr)
set.seed(20)
# Features are scaled and demeaned,
# then centralized around the mean within cross-sections (fixed time effects)
data_prepared <- bdsm::economic_growth[, 1:5] %>%
bdsm::feature_standardization(
excluded_cols = c(country, year, gdp)
) %>%
bdsm::feature_standardization(
group_by_col = year,
excluded_cols = country,
scale = FALSE
)The function optim_model_space() estimates all possible
models (each possible subset of regressors) via maximum likelihood,
storing the results in a list object. For small to moderately sized
datasets:
model_space <- bdsm::optim_model_space(
df = data_prepared,
dep_var_col = gdp, # Dependent variable
timestamp_col = year,
entity_col = country,
init_value = 0.5,
)For larger datasets, you can leverage multiple cores:
library(parallel)
# Choose an appropriate number of cores, taking into account system-level limits
cores <- as.integer(Sys.getenv("_R_CHECK_LIMIT_CORES_", unset = NA))
if (is.na(cores)) {
cores <- detectCores()
} else {
cores <- min(cores, detectCores())
}
cl <- makeCluster(cores)
clusterEvalQ(cl, library(bdsm))
#> [[1]]
#> [1] "bdsm" "stats" "graphics" "grDevices" "utils" "datasets"
#> [7] "methods" "base"
#>
#> [[2]]
#> [1] "bdsm" "stats" "graphics" "grDevices" "utils" "datasets"
#> [7] "methods" "base"
#>
#> [[3]]
#> [1] "bdsm" "stats" "graphics" "grDevices" "utils" "datasets"
#> [7] "methods" "base"
#>
#> [[4]]
#> [1] "bdsm" "stats" "graphics" "grDevices" "utils" "datasets"
#> [7] "methods" "base"
#>
#> [[5]]
#> [1] "bdsm" "stats" "graphics" "grDevices" "utils" "datasets"
#> [7] "methods" "base"
#>
#> [[6]]
#> [1] "bdsm" "stats" "graphics" "grDevices" "utils" "datasets"
#> [7] "methods" "base"
#>
#> [[7]]
#> [1] "bdsm" "stats" "graphics" "grDevices" "utils" "datasets"
#> [7] "methods" "base"
#>
#> [[8]]
#> [1] "bdsm" "stats" "graphics" "grDevices" "utils" "datasets"
#> [7] "methods" "base"
model_space <- bdsm::optim_model_space(
df = data_prepared,
timestamp_col = year,
entity_col = country,
dep_var_col = gdp,
init_value = 0.5,
cl = cl
)
stopCluster(cl)A progress bar is displayed to easily track the ongoing computation.
After preparing the model space, run bma() to obtain
posterior model probabilities, posterior inclusion probabilities (PIPs),
and other BMA statistics under the binomial and
binomial-beta model priors:
bma_results <- bdsm::bma(model_space, df = data_prepared, round = 3)
# Inspect the BMA summary (binomial prior results first, binomial-beta second)
bma_results[[1]] # BMA stats under binomial prior
#> PIP PM PSD PSDR PMcon PSDcon PSDRcon %(+)
#> gdp_lag NA 1.078 0.110 0.229 1.078 0.110 0.229 100
#> ish 0.710 0.085 0.061 0.090 0.120 0.032 0.085 100
#> sed 0.714 -0.046 0.061 0.111 -0.065 0.064 0.127 0
bma_results[[2]] # BMA stats under binomial-beta prior
#> PIP PM PSD PSDR PMcon PSDcon PSDRcon %(+)
#> gdp_lag NA 1.078 0.110 0.239 1.078 0.110 0.239 100
#> ish 0.765 0.091 0.058 0.090 0.120 0.033 0.085 100
#> sed 0.768 -0.048 0.062 0.114 -0.063 0.064 0.126 0
# Posterior model sizes:
bma_results[[16]]
#> Prior model size Posterior model size
#> Binomial 1 1.424
#> Binomial-beta 1 1.533Key columns in the BMA output include: - PIP: Posterior inclusion probability for each regressor. - PM: Posterior mean of each parameter (averaged over all models). - PSD/PSDR: Posterior standard deviations (regular/robust) of each parameter - %(+): Percentage of models (among those that include a given regressor) in which the parameter estimate is positive.
model_pmp(): Shows prior vs. posterior
model probabilities, ranking models from best to worst.model_sizes(): Displays how prior
vs. posterior probabilities mass is distributed across different model
sizes.# Plot prior vs. posterior model probabilities
pmp_graphs <- bdsm::model_pmp(bma_results, top = 3) # Show top 3 models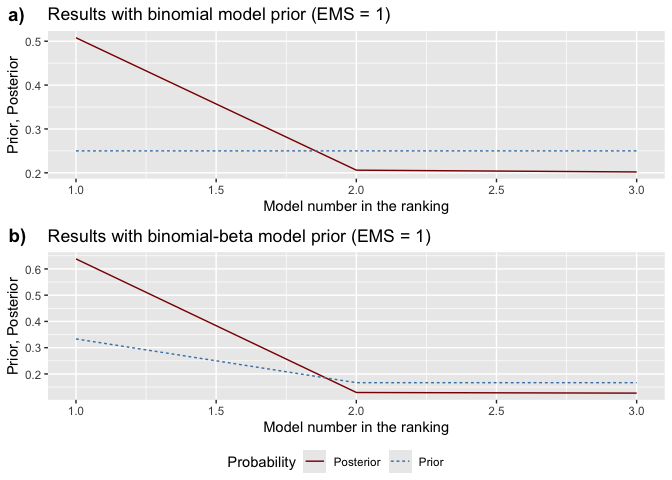
# Plot probabilities by model size
size_graphs <- bdsm::model_sizes(bma_results)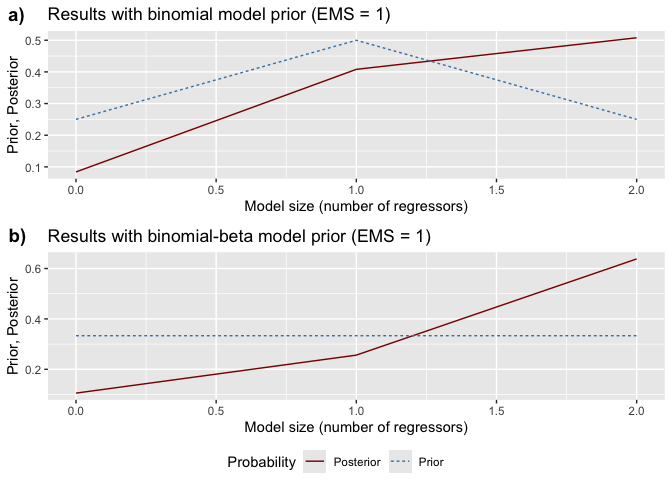
Use best_models() to extract specific information about
the top-ranked models:
# Retrieve the 5 best models according to binomial prior
top3_binom <- bdsm::best_models(bma_results, criterion = 1, best = 3)
# Print the inclusion matrix for each of the top 3 models
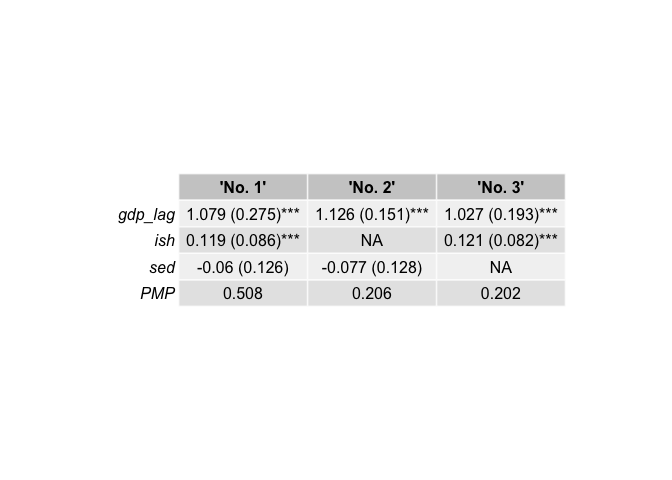
top3_binom[[1]]
#> 'No. 1' 'No. 2' 'No. 3'
#> gdp_lag 1.000 1.000 1.000
#> ish 1.000 0.000 1.000
#> sed 1.000 1.000 0.000
#> PMP 0.508 0.206 0.202
# Retrieve robust standard errors in a knit-friendly table
top3_binom[[6]]| ‘No. 1’ | ‘No. 2’ | ‘No. 3’ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| gdp_lag | 1.079 (0.275)*** | 1.126 (0.151)*** | 1.027 (0.193)*** |
| ish | 0.119 (0.086)*** | NA | 0.121 (0.082)*** |
| sed | -0.06 (0.126) | -0.077 (0.128) | NA |
| PMP | 0.508 | 0.206 | 0.202 |
Assess whether two regressors tend to co-occur (complements) or
exclude each other (substitutes) using jointness(). By
default, it calculates the Hofmarcher et al. (2018) measure:
joint_measures <- bdsm::jointness(bma_results)
head(joint_measures)
#> ish sed
#> ish NA 0.159
#> sed 0.505 NAYou can also specify older measures, such as "LS" (Ley
& Steel) or "DW" (Doppelhofer & Weeks):
joint_measures_ls <- bdsm::jointness(bma_results, measure = "LS")Below is a minimal reproducible workflow:
# 1) Data preparation
data_prepared <- bdsm::economic_growth[, 1:5] %>%
bdsm::feature_standardization(
excluded_cols = c(country, year, gdp)
) %>%
bdsm::feature_standardization(
group_by_col = year,
excluded_cols = country,
scale = FALSE
)
# 2) Estimate model space
model_space <- bdsm::optim_model_space(
df = data_prepared,
dep_var_col = gdp,
timestamp_col = year,
entity_col = country,
init_value = 0.5,
)
# 3) Run Bayesian Model Averaging
bma_obj <- bdsm::bma(
model_space = model_space,
df = data_prepared
)
# 4) Inspect the top 3 models under binomial prior
best_3 <- bdsm::best_models(
bma_list = bma_obj,
criterion = 1,
best = 3
)
best_3[[1]] # Inclusion table
#> 'No. 1' 'No. 2' 'No. 3'
#> gdp_lag 1.000 1.000 1.000
#> ish 1.000 0.000 1.000
#> sed 1.000 1.000 0.000
#> PMP 0.508 0.206 0.202
best_3[[2]] # Coefficients & standard errors
#> 'No. 1' 'No. 2' 'No. 3'
#> gdp_lag "1.079 (0.111)***" "1.126 (0.106)***" "1.027 (0.093)***"
#> ish "0.119 (0.033)***" NA "0.121 (0.03)***"
#> sed "-0.06 (0.063)" "-0.077 (0.063)" NA
#> PMP "0.508" "0.206" "0.202"Make sure to go through the displayed errors. The problem might be connected to your OS environment. E.g. you might see an information like the following:
Configuration failed to find one of freetype2 libpng libtiff-4 libjpeg. Try installing:
* deb: libfreetype6-dev libpng-dev libtiff5-dev libjpeg-dev (Debian, Ubuntu, etc)
* rpm: freetype-devel libpng-devel libtiff-devel libjpeg-devel (Fedora, CentOS, RHEL)
* csw: libfreetype_dev libpng16_dev libtiff_dev libjpeg_dev (Solaris)In such case you should first try installing the recommended packages. With properly configured system environment everything should work fine.
(Additional references related to the methodology can be found in the package vignette.)
We welcome bug reports, feature requests, and contributions. Feel free to open an issue or pull request on GitHub.
This package is distributed under the GPL (\(\geq 2\)) license. See the LICENSE file for details.